লিমিট (Limit)
লিমিট কি? (Limit)
y=f(x) এর x চলকেরে মান একটি নির্দিষ্ট ধ্রুব সংখ্যা a অপেক্ষা বৃহত্তর বা ক্ষুদ্রতর মানগুলি গ্রহণ করে ক্রমশ a এর নিকটবর্তী হওয়ায় যদি f (x) ফাংশনের মান আরেকটি ধ্রুবক l এর নিকটবর্তী হয় তবে 1 কে f (x) ফাংশনের সীমা/limit বলে।
\Rightarrow একে প্রকাশ করা হয় l t / \lim দ্বারা।
\operatorname{Lim} f(x)=l \rightarrow সীমাস্থমান।
যেমনঃ
f(x)=\frac{x^{2}-4}{x-2}
\frac{\lim }{x \rightarrow 0} f(x) = \frac{\lim }{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{x^{2}-4}{x-2}
| x | f(x) |
| 2 | \alpha |
| 1.9 | 3.9 |
| 1.9999 | 3.9999 |
| 2.01 | 4.01 |
| 2.000001 | 4.000001 |
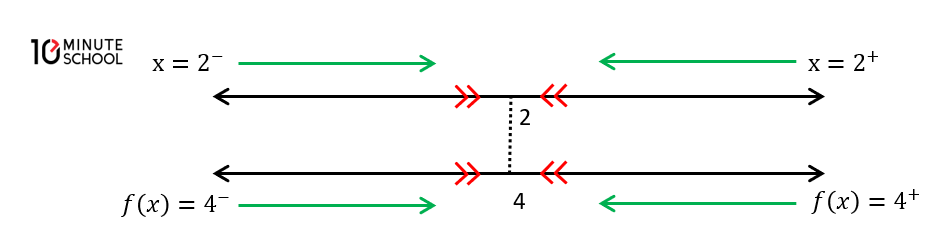
⟹ বামদিকবর্তী লিমিট (The limit on the left) :
x চলক a অপেক্ষায় ক্ষুদ্রতম মান গ্রহন করে বামদিক হতে ক্রমশ a এর নিকটবর্তী হওয়ায় যদি f (x) ফাংশনের মান ধ্রুবক 1 এর নিকটবর্তী হয় তবে 1 কে f (x) ফাংশনের বামদিকবর্তী বা বামাবর্তী লিমিট বলে।
\frac{\operatorname{Lim}}{x \rightarrow a^{-}} f(x) =l
⟹ ডানদিকবর্তী লিমিট (The limit on the right) :
x চলক a অপেক্ষায় বৃহত্তম মানগুলি গ্রহন করে ডানদিক হতে ক্রমশ a ‘ এর নিকটবর্তী হওয়ায় যদি f (x) ফাংশনের মান ধ্রুবক 1 এর নিকটবর্তী হয় তবে 1 কে f (x) ফাংশনের ডানদিকবর্তী বা ডানাবর্তী লিমিট বলে।
\frac{\operatorname{Lim}}{x \rightarrow a^{+}} f(x) =l
⟹ সীমার মৌলিক ধর্মাবলী (The basic religions of the range):
\frac{\operatorname{lim}}{x \rightarrow a} f(x)= l এবং \frac{\operatorname{Lim}}{x \rightarrow a} g(x)=m
1. \frac{\operatorname{lim}}{x \rightarrow a}\{f(x) \pm g(x)\} =\frac{\operatorname{Lim}}{x \rightarrow a} f(x) \pm \frac{\operatorname{Lim}}{x \rightarrow a} g(x) j =l \pm m
2.\frac{\operatorname{lim}}{x \rightarrow a} c f(x) =c \frac{\operatorname{Lim}}{x \rightarrow a} f(x) ; c=ধ্রুবক
3. \frac{\operatorname{lim}}{x \rightarrow a} f(x) g(x) =\frac{\operatorname{Lim}}{x \rightarrow a} f(x) \cdot \frac{\operatorname{Lim}}{x \rightarrow a} g(x) =\operatorname{lm}
4.\frac{\lim }{x \rightarrow a} \frac{1}{f(x)} =\frac{1}{l} ; if l \neq 0
5. \frac{\operatorname{lim}}{x \rightarrow a} \frac{f(x)}{g(x)}=\frac{l}{m} ; if m \neq 0
6. \frac{\operatorname{lim}}{x \rightarrow a} c=c ; \mathrm{c}= \text {ধ্রুবক}
এইচএসসি ও এডমিশন পরীক্ষার্থীদের জন্য আমাদের কোর্সসমূহঃ
- HSC 25 অনলাইন ব্যাচ ২.০ (বাংলা, ইংরেজি, তথ্য ও যোগাযোগ প্রযুক্তি)
- HSC 26 অনলাইন ব্যাচ (বাংলা, ইংরেজি, তথ্য ও যোগাযোগ প্রযুক্তি)
- HSC 25 অনলাইন ব্যাচ (ফিজিক্স, কেমিস্ট্রি, ম্যাথ, বায়োলজি)
- HSC 26 অনলাইন ব্যাচ (ফিজিক্স, কেমিস্ট্রি, ম্যাথ, বায়োলজি)
- মেডিকেল এডমিশন কোর্স – ২০২৪
- ঢাকা ভার্সিটি A Unit এডমিশন কোর্স – ২০২৪
- ঢাকা ভার্সিটি B Unit এডমিশন কোর্স – ২০২৪
- বুয়েট কোশ্চেন সলভ কোর্স
- গুচ্ছ A Unit এডমিশন কোর্স – ২০২৪
- গুচ্ছ B Unit এডমিশন কোর্স – ২০২৪
আমাদের স্কিল ডেভেলপমেন্ট কোর্সসমূহঃ
- বিদেশে উচ্চশিক্ষা: Study Abroad Complete Guideline
- Student Hacks
- IELTS Course by Munzereen Shahid
- Complete English Grammar Course
- Microsoft Office 3 in 1 Bundle
- ঘরে বসে Freelancing
- Facebook Marketing
- Adobe 4 in 1 Bundle
১০ মিনিট স্কুলের ক্লাসগুলো অনুসরণ করতে ভিজিট: www.10minuteschool.com
